Adding CSS To Your HTML
For beginners … very picture heavy since CSS is such a visual discipline!
Adding CSS To Your HTML
For beginners … very picture heavy since CSS is such a visual discipline
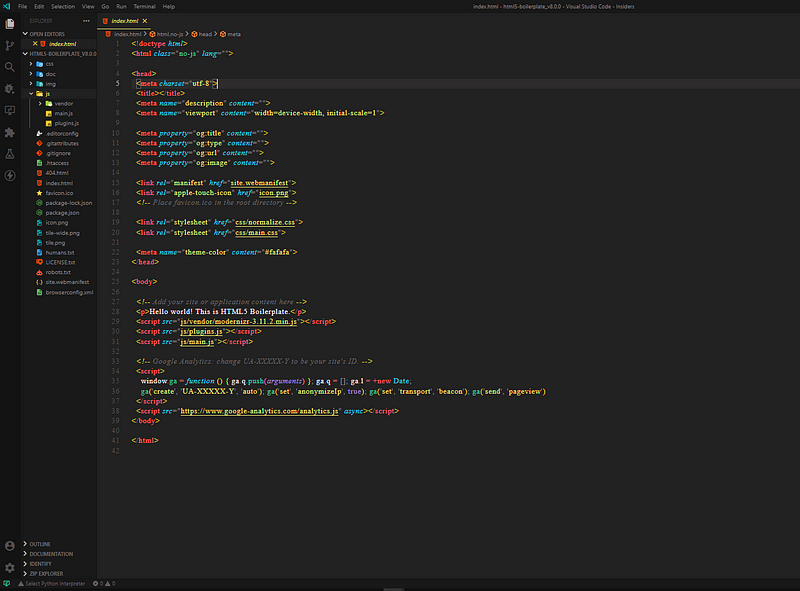
<!-- example.html -->
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<link
rel="stylesheet"
href="https://cdnjs.cloudflare.com/ajax/libs/normalize/3.0.3/normalize.min.css"
/>
<link rel="stylesheet" href="/styles/site.css" />
</head>
<body>- To connect your CSS sheet to your HTML page, use the link tag like so.
- Many developers use External pre-written CSS stylesheets for consistent design.
- You can connect multiple stylesheets.
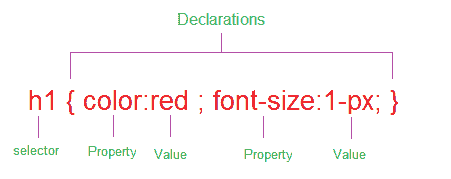
CSS Selectors
CSS Selector: Applies styles to a specific DOM element(s), there are various types:Type Selectors: Matches by node name.

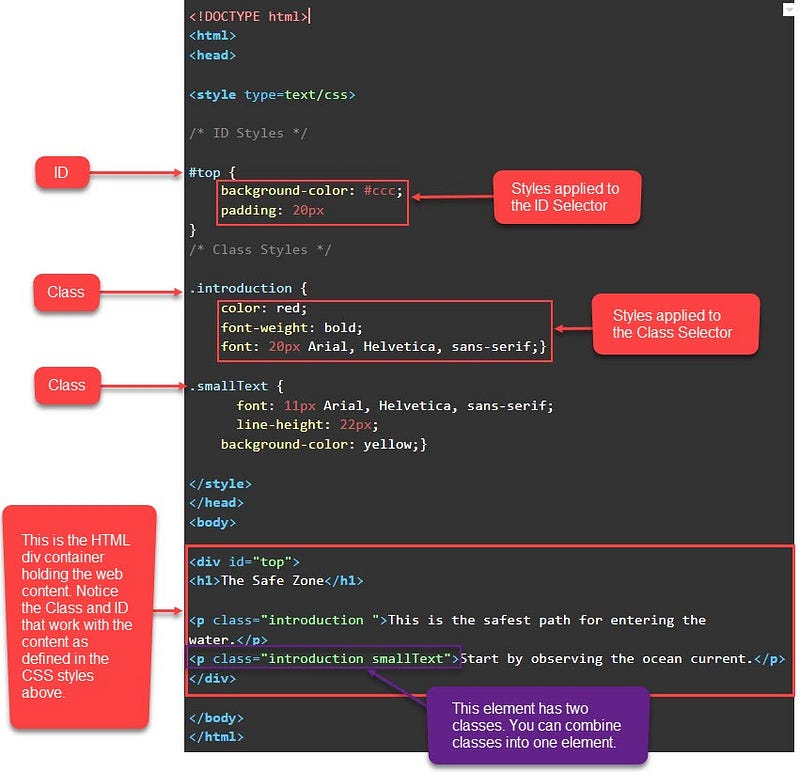
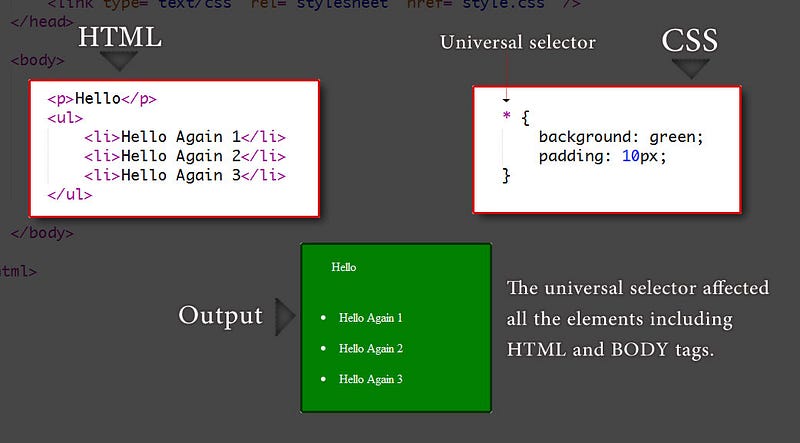
/* Type selector */
div {
background-color: #000000;
}
/* Class selector */
.active {
color: #ffffff;
}
/* ID selector */
#list-1 {
border: 1px solid gray;
}
/* Universal selector */
* {
padding: 10px;
}
/* Attribute selector */
a[title] {
font-size: 2em;
}Class Selectors
- Used to select all elements of a certain class denoted with a
.[class name] - You can assign multiple classes to a DOM element by separating them with a space.
Compound Class Selectors
<div class="box yellow">- i.e. .box.yellow will select only the first element.
- KEEP IN MIND that if you do include a space it will make the selector into a descendant selector.
h1#heading,
h2.subheading {
font-style: italic;
}- When we want to target all
h1tags with the id ofheading.
CSS Combinators
- CSS Combinators are used to combine other selectors into more complex or targeted selectors — they are very powerful!
- Be careful not to use too many of them as they will make your CSS far too complex.
Descendant Selectors

Direct Child Selectors

CSS
.menu > .is-active { background-color: #ffe0b2; }HTML
<body> <div class="menu"> <div class="is-active">Belka</div> <div> <div class="is-active">Strelka</div> </div> </div> </body> <div class="is-active"> Laika </div> </body>- Belka would be the only element selected.
Adjacent Sibling Selectors

h1 + h2 { font-style: italic; }
//HTML:
<h1>Big header</h1> <h2>This one is styled because it is directly adjacent to the H1</h2> <h2>This one is NOT styled because there is no H1 right before it</h2>
h1 + h2 { font-style: italic; }
<h1>Big header</h1> <h2>This one is styled because it is directly adjacent to the H1</h2> <h2>This one is NOT styled because there is no H1 right before it</h2>Pseudo-Classes
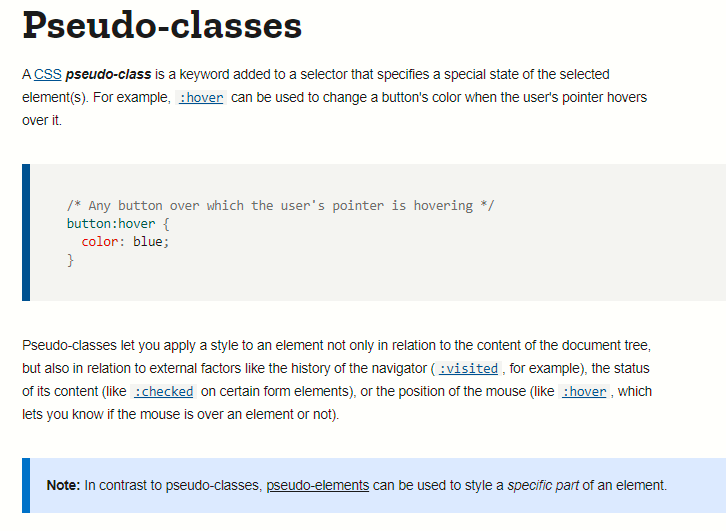
a:hover {
font-family: "Roboto Condensed", sans-serif;
color: #4fc3f7;
text-decoration: none;
border-bottom: 2px solid #4fc3f7;
}Some common pseudo-classes that are frequently used are:
active: 'push down', when elements are activated.checked: applies to things like radio buttons or checkbox inputs.



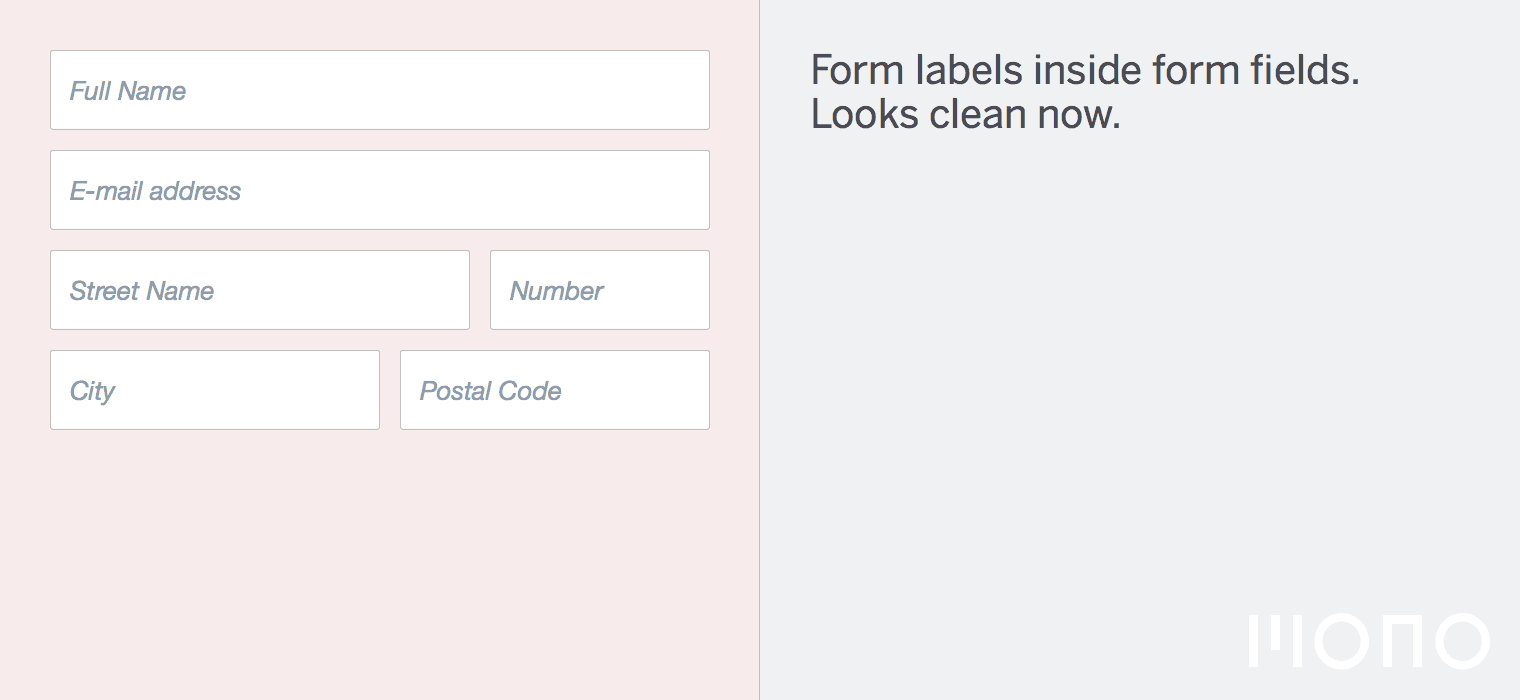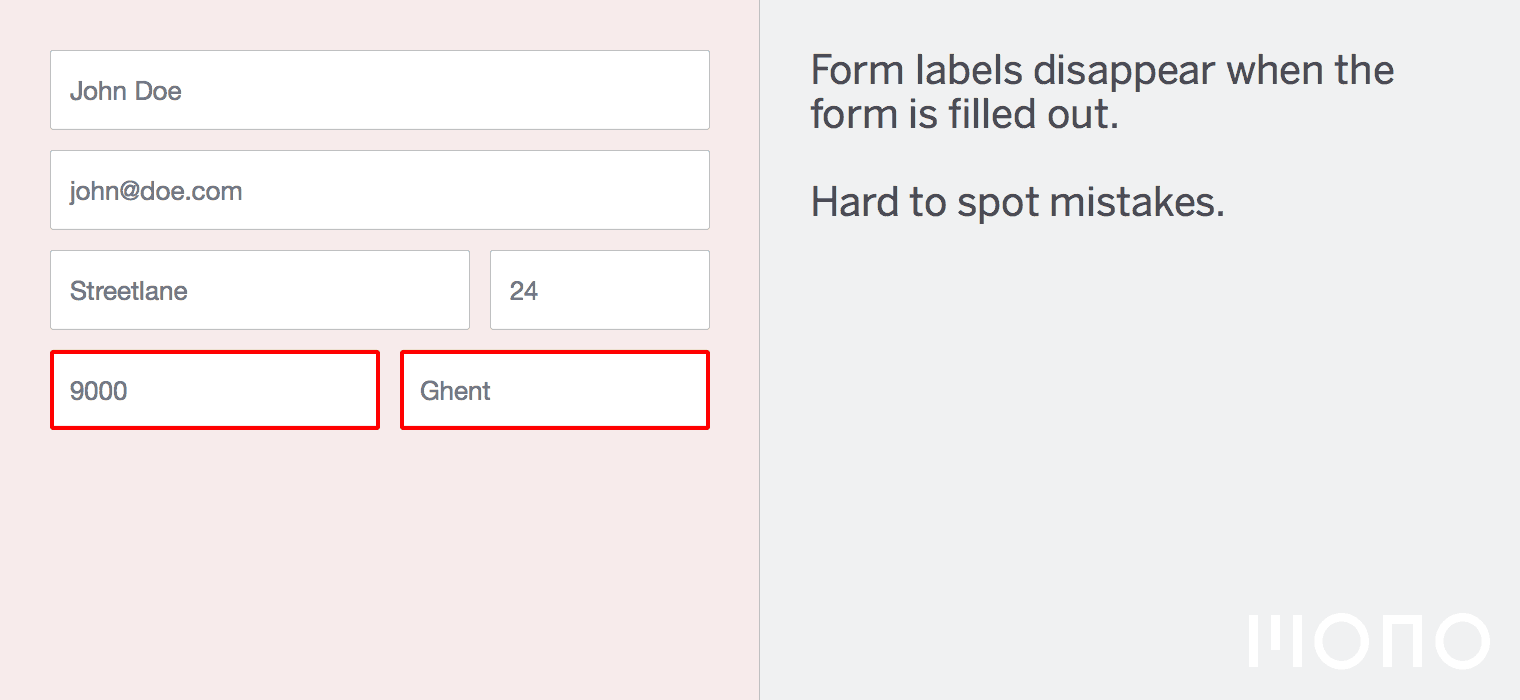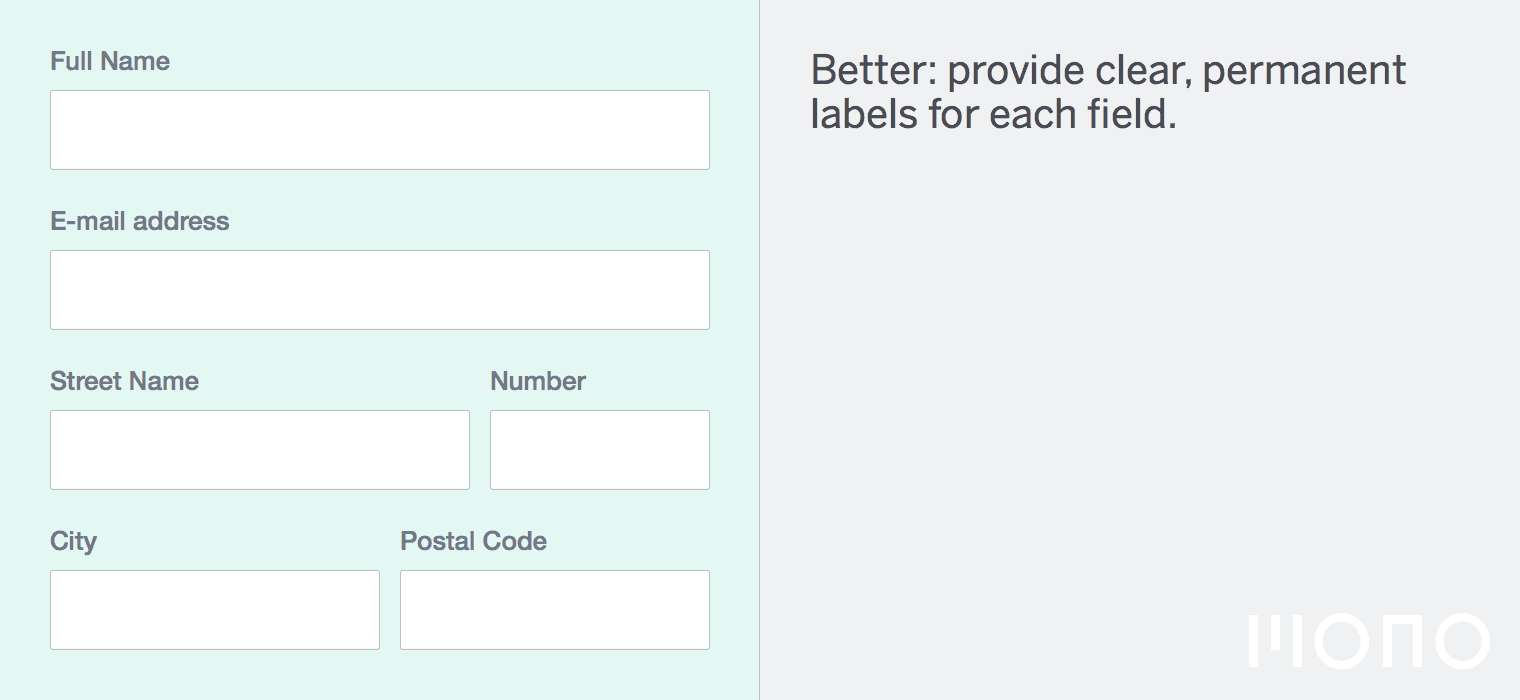
Pseudo-Selectors
- Used to create pseudo-elements as children of the elements to which the property applies.
::after::before
<style>
p::before {
background-color: lightblue;
border-right: 4px solid violet;
content: ":-) ";
margin-right: 4px;
padding-left: 4px;
}
</style>
<p>This is the first paragraph</p>
<p>This is the second paragraph</p>
<p>This is the third paragraph</p>- Will add some blue smiley faces before the p tag elements.
CSS Rules
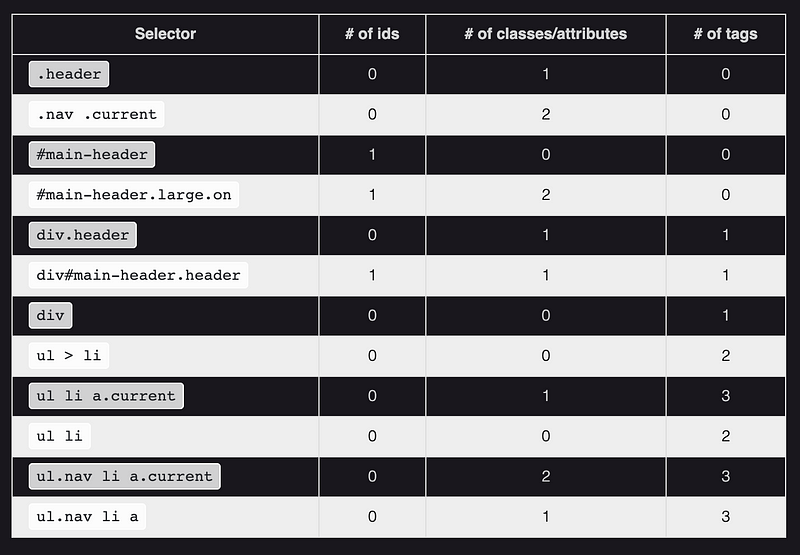
CSS Rule: Collection of single or compound selectors, a curly brace, zero or more propertiesCSS Rule Specificity: Sometimes CSS rules will contain multiple elements and may have overlapping properties rules for those same elements - there is an algorithm in CSS that calculates which rule takes precedence.The Four Number Calculation: listed in increasing order of importance.- Who has the most IDs? If no one, continue.
- Who has the most classes? If no one, continue.
- Who has the most tags? If no one, continue.
- Last Read in the browser wins.
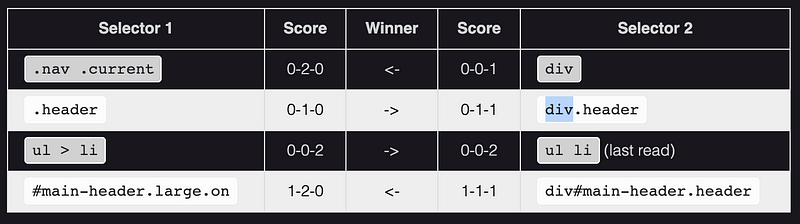
- Coming back to our example where all the CSS Rules have tied, the last step 4 wins out so our element will have a
purple border.
CSS: Type, Properties, and Imports
Typography
font-family: change the font.
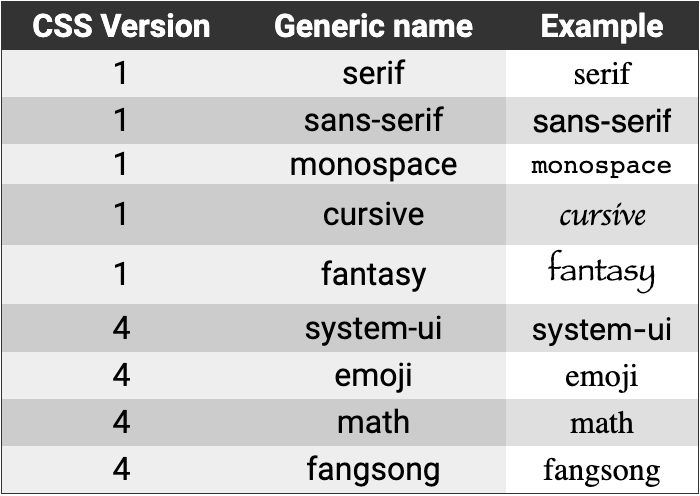
Background-Images
- You can use the background-image property to set a background image for an element.
CSS: Colors, Borders, and Shadows
Colors
- You can set colors in CSS in three popular ways: by name, by hexadecimal RGB value, and by their decimal RGB value.
- rgba() is used to make an rbg value more transparent, the
ais used to specify thealpha channel. - Color : Property used to change the color of text.
- Background-Color : Property to change the backgrounf color of an element.
Borders
- Borders take three values: The width of the border, the style (i.e. solid, dotted, dashed), color of the border.
Shadows
- There are two kinds of shadows in CSS:
box shadowsandtext shadows. - Box refers to HTML elements.
- Text refers to text.
- Shadows take values such as, the horizontal & vertical offsets of the shadow, the blur radius of the shadow, the spread radius, and of course the colors.
My Blog
Web-Dev-Hubmy resource sharing and blog site ... centered mostly on web development and just a bit of audio production / generally…bgoonz-blog.netlify.app
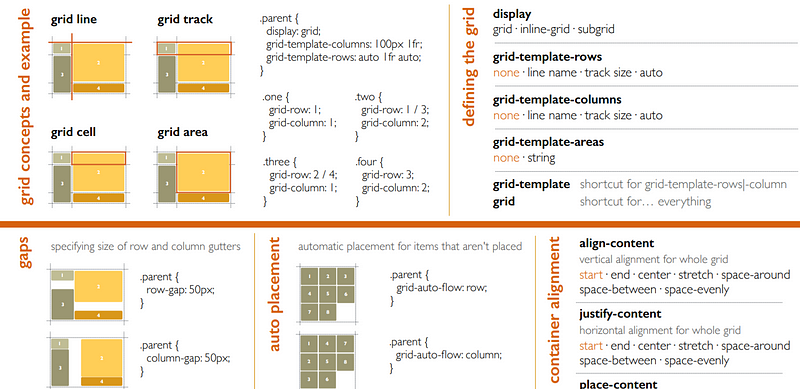
Grid Cheat Sheet